PEST Analysis in Marketing: Template, Examples & More
Summer Nguyen | 03-17-2025

When evaluating whether a business idea or strategy is feasible, it’s essential to consider all factors that could affect your business, both positively and negatively. You need to weigh the pros and cons of the project or idea—those that can contribute to its success or lead to its failure. This is where a PEST Analysis comes into play.
In this article, you’ll learn everything you need to know about conducting a PEST Analysis and how to apply it to your business.
What is PEST Analysis?
PEST analysis is a management tool that helps organizations assess key external factors —political, economic, social, and technological—that impact their operations. By understanding these areas, businesses can enhance their competitiveness in the market.
A common variation, particularly in the U.K., is the PESTLE approach, which adds two more factors: legal and environmental. PEST analysis is based on the idea that thoroughly assessing the key factors impacting both an organization and its industry can lead to more effective strategic planning. By understanding these influences, organizations can better capitalize on current conditions and be prepared for upcoming changes, helping them stay ahead of competitors.
4 Elements of PEST Analysis

1. Political (P)
In this part of the PEST analysis, you examine government regulations and legal factors that influence the business environment and trade markets, which can greatly impact your business operations. Key issues to consider include property rights, political stability, tax changes, safety regulations, trade laws, and employment laws. Important questions to ask might include, “Could any pending legislation or tax changes affect your business?” or “Are there changes in business laws or trade regulations that could disrupt your operations?”

A PEST analysis explores key political factors that can affect businesses, such as:
- Government policies: Local, national, and international policies like tax laws, environmental regulations, labor laws, and trade policies can impact business costs, operations, and market access.
- Political stability: A stable political environment fosters business confidence and growth, while instability creates uncertainty and discourages investment.
- Government leadership: The views of government leaders can shape business practices, such as tightening regulations on polluting industries or incentivizing sustainable practices.
- Trade restrictions and reforms: Changes in trade agreements, tariffs, and import/export rules can either restrict or create new opportunities for international businesses.
2. Economic ( E)
Economic factors are indispensable in determining how a business operates and its profitability. These factors include inflation, economic growth, exchange rates, interest rates, taxation, unemployment, and access to credit. By analyzing these elements, businesses can assess potential impacts on their operations.

A PEST analysis helps explore key economic factors such as:
- Economic growth: Influences consumer spending, investment, and business profitability based on whether the economy is expanding, stagnating, or declining.
- Inflation: Affects business costs, consumer purchasing power, and investment decisions.
- Interest rates: Determine the cost of borrowing, impacting businesses’ ability to invest and expand.
- Exchange rates: Influence import/export costs and international trade competitiveness.
- Consumer spending: Drives demand for products and services, affecting business revenue.
- Unemployment: Impacts consumer spending power and labor availability.
- Taxation: Affects business costs and profitability through government-imposed taxes.
- Access to credit: Influences investment and spending by affecting the availability and cost of credit for businesses and consumers.
3. Social (S)
Social factors, also known as sociocultural factors, help businesses understand their market’s social and economic environment. These include customer demographics, lifestyle choices, career attitudes, population growth, religious beliefs, cultural norms, ethnic backgrounds, location, and education. By analyzing these, businesses can identify customer needs, understand what attracts them to products or services, and estimate market potential. Consider asking, “Are there any social factors that could influence change in your business?”

A PEST analysis examines various social factors that can impact businesses, such as:
- Demographics: Population characteristics like age, gender, income, education, and family size help businesses tailor products, services, and marketing to specific target groups.
- Cultural values and attitudes: Societal norms and beliefs influence consumer habits and workplace dynamics, making cultural sensitivity essential for market success.
- Lifestyle trends: Shifts in lifestyle, like work-life balance, health focus, and environmental awareness, can change consumer demand, requiring businesses to adapt their offerings.
- Consumer preferences: Changes in buying habits, such as the rise of online shopping and ethical consumerism, may require adjustments in business models and product development.
- Social media and Internet usage: The influence of social media and the Internet on consumer behavior and brand perception makes it vital for businesses to use these platforms to reach their audiences effectively.
4. Technological (T)
Technological factors, including changes, innovations, and advancements, can impact businesses both positively and negatively. By identifying new technologies and adapting them, businesses can stay competitive while phasing out obsolete ones.
A PEST analysis looks at key technological factors that affect businesses, such as:
- Emerging technologies: Innovations like AI, automation, and IoT can transform industries. Businesses must assess these technologies’ impact to stay competitive.
- Rate of technological change: Rapid advancements require businesses to be adaptable, invest in R&D, and stay updated on industry trends.
- Access to technology: The availability of tech and infrastructure, like high-speed internet and cloud computing, affects a business’s ability to innovate and compete.
- Cybersecurity: As reliance on technology grows, so do cybersecurity threats, making strong protection measures essential.
- Communication impact: Technology influences how businesses communicate with customers and partners, enhancing collaboration and engagement.
Examples of a PEST Analysis
Renewable Energy Company
- Political: Government incentives, subsidies, and regulations for renewable energy, including compliance with frameworks like RED III (Renewable Energy Directive III).
- Economic: Energy prices, carbon emissions trading, and economic growth.
- Socio-Cultural: Public perception of renewable energy, environmental awareness, and energy efficiency trends.
- Technological: Advancements in solar, wind, and battery technology.
A Tech Startup
- Political: Government regulations on data privacy, cybersecurity, and technology infrastructure.
- Economic: Economic growth, interest rates, and consumer spending patterns.
- Socio-Cultural: Changing consumer preferences, digital literacy, and social media trends.
- Technological: Innovations in artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and mobile technology.
Main Applications of PEST Analysis
1. Work as an Input for SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis refers to identifying and analyzing the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats associated with your project, goal, or situation. This process helps determine how these factors might impact your initiative.
To conduct an effective SWOT analysis, it’s common to first perform a PEST analysis. The insights gained from PEST analysis, which examines external factors on a macro level, are then used as input for the SWOT analysis. In contrast, SWOT focuses on internal factors at a more detailed, micro level, such as for a specific product, project, or activity.
2. Assess regular external risk
Internal risks are easier to spot due to the available data within the company. However, external threats are beyond the company’s control and can be difficult to track. If these risks become issues, they can disrupt the organization’s plans and strategies. PESTEL analysis offers a structured way to identify and address these hidden risks and challenges. As a key part of strategic management, PESTEL analysis helps reduce potential market risks and ensures business plans are carried out smoothly.
3. Understand the business environment deeper
PEST analysis will help you identify the direct and indirect environments affecting your business that could be unnoticed. You may not realize how your products work well in their current situation while being unsuccessful on another side of the country. PEST analysis enables you to see the big picture of all the external factors that affect your business, either positively or negatively.
4. Take advantage of new opportunities
PEST analysis helps you identify and seize opportunities by understanding the broader business environment. This knowledge allows you to recognize and capitalize on opportunities, helping you stay competitive.
Best practice for PEST Analysis
PEST analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps businesses understand external factors affecting their performance. Let’s dive into how to do a PEST analysis in 4 simple steps.
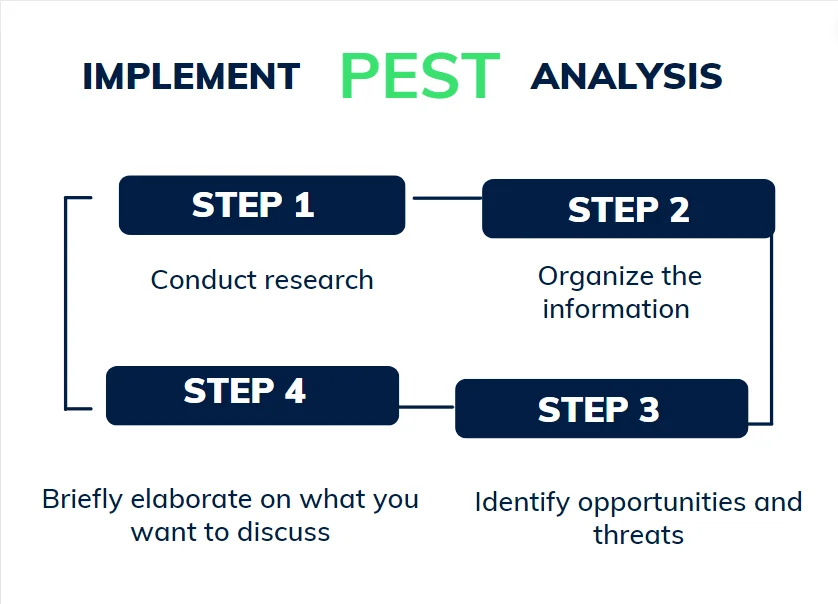
Step 1: Conduct research
Start by gathering all relevant information for each PEST category—political, economic, social, and technological factors. This research stage is crucial, so take your time and involve colleagues from different departments to ensure a thorough analysis. Although this step may be time-consuming, the valuable insights gained will help you fine-tune your strategy.
Step 2: Organize the information
Next, categorize the data you’ve collected. For example, inflation rates belong under economic factors, political unrest under political factors, and new software under technological factors. Use lists or an affinity diagram to organize the information in a way that allows you to easily summarize and share it with stakeholders.
Step 3: Identify opportunities and threats
With the information organized, identify how these external factors impact your business. Determine which factors present opportunities, like new technology or market expansion, and which pose threats, such as economic instability.
Step 4: Apply your insights
Finally, use the insights from your analysis to adapt your business strategy. Integrate the findings into your strategic plan or other frameworks like a business model canvas, ensuring that your approach addresses both the opportunities and threats identified.
PEST Analysis vs SWOT Analysis
This chart highlights the main differences and uses of SWOT and PEST analyses in strategic planning:
| Aspect | SWOT Analysis | PEST Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Internal factors of an organization | External factors of the environment |
| Components | Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats | Political, Economic, Social, Technological |
| Purpose | Identify internal strong points and weak points, as well as external opportunities and threats | Assess broad external influences on business |
| Scope | Micro-level (specific projects, businesses) | Macro-level (overall environment) |
| Use case | Strategic planning, risk management | Environmental scanning, strategic planning |
In conclusion, SWOT Analysis focuses on the internal factors of an organization (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), while PEST Analysis examines external environmental factors (Political, Economic, Social, and Technological). By combining these two analyses, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their position and develop effective strategies.
FAQs
1. What are the economic factors in PEST analysis?
Economic factors within a PEST analysis encompass financial or economic aspects that could affect your business activities. They include:
- Political factors: Government regulations, stability, trade policies.
- Economic factors: Economic growth, inflation rates, exchange rates.
- Social factors: Demographic trends, cultural attitudes, lifestyle changes.
- Technological factors: Innovation, automation, technological advancements.
2. What is a PEST analysis diagram?
A PEST analysis diagram serves as a structure for recognizing potential political, economic, social, and technological shifts that could affect your business in the future. By conducting this analysis, you can proactively adapt your business strategies to keep pace with the constantly evolving external landscape.
3. How often should a PEST analysis be conducted?
The frequency of conducting a PEST analysis can vary depending on factors such as the industry, market dynamics, and business objectives. However, it’s generally recommended to conduct it regularly, at least annually, or whenever there are significant changes in the operating environment.
4. What are the limitations of a PEST analysis?
While PEST analysis provides valuable insights, it may oversimplify complex issues and overlook other important factors such as legal, environmental, and ethical considerations. Additionally, the analysis may be subjective and prone to biases based on the perspectives of those conducting it. Therefore, it’s important to use PEST analysis in conjunction with other strategic tools and approaches for a comprehensive understanding of the business environment.
Final Words
Running a business is not an easy task. You do not just have to deal with the problems within your company; external factors that impact your business’s operation and success also need to be taken into consideration. PEST Analysis is a useful tool to make this process easier. I hope that this article helps you understand PEST analysis to the fullest and that you can make an intuitive PEST analysis for your business. Thank you for reading.






