What is Marketing? Types, Strategies & Best Practices!

What Is Marketing?

Marketing is everything you do to promote your business and encourage customers to buy your products or services. It’s about understanding your target audience, offering what they want, and creating great experiences to keep them coming back.
Marketing focuses on learning about customers and their behavior. The goal is to attract, win, and keep customers by meeting their needs. This can include activities like advertising, social media, building relationships, creating promotions, and making sure products are available where customers need them.
Why Do Companies Need to Implement Marketing?
Marketing is essential for gaining customers and boosting sales. It involves every step of delivering a product or service, including the marketing mix:
- What products to sell
- Which channels to use
- Pricing strategies
- Promotion
A tailored marketing strategy ensures your product or service reaches the right audience. Here’s how it helps:
1. Boost Sales
Products that aren’t marketed are harder to sell. Strategies like email campaigns, social media updates, and online listings help attract potential customers and expand your reach.
2. Inform Consumers
Marketing educates customers about your business, showing why they should choose you over competitors. It highlights your product’s benefits, your brand’s mission, and how you solve customer problems.
3. Engage Consumers
Marketing builds lasting relationships with customers, turning one-time buyers into loyal clients. Social media is powerful for increasing website traffic, engaging customers, and retargeting them with posts and updates after purchases.
4. Build Reputation
A strong reputation attracts customers. Marketing helps establish trust by showcasing your mission and values, strengthening your brand’s credibility.
5. Grow Your Business
Effective marketing drives revenue growth by educating, engaging, and selling strategically. It’s a key tool for acquiring new customers and sustaining business success.
In short, marketing generates interest in your products or services through research, analysis, and understanding of your ideal customers. It influences every part of your business, from product development to sales and advertising, making it vital for long-term success.
Types of Marketing
There are two main types of marketing: digital and traditional. While both have their unique advantages, digital marketing has become more practical and dominant in today’s modern era—especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, which significantly accelerated the growth of e-commerce.
So, we’ll talk about digital marketing first.
Digital Marketing
Digital marketing includes promoting and selling products or services via online platforms such as social media, email, and search engines. Its key parts include:
1. Search Engine Optimization Marketing
SEO focuses on boosting a website’s ranking on SERPs (search engine results pages) by improving its content and structure. Since most users don’t go beyond the first page of results, appearing higher is critical.
Types of SEO:
- 1. On-page SEO: Optimizing website content, including headers, meta descriptions, and keyword placement.
- 2. Off-page SEO: Building backlinks and social media shares to boost website authority.
- 3. Technical SEO: Improving technical factors like site speed, mobile-friendliness, and avoiding duplicate content. SEO typically requires 3-6 months to show significant results, making it ideal for businesses focused on long-term growth rather than short-lasting and trending campaigns.
2. Content Marketing
Content marketing focuses on educating, persuading, and entertaining customers through digital content. The goal is to guide the audience throughout the marketing funnel, from the very first step of having awareness about your brand to conversion, using written, video, or audio content.
Tailored Content for Different Audiences:
- B2B Companies: Often target decision-makers and use data-driven formats like blog posts, reports, case studies, infographics, videos, e-books, and white papers.
- B2C Companies: Focus more on engaging formats like blog posts, quizzes, fun videos, and e-books.
3. Email Marketing

Email marketing involves sending promotional and informational messages directly to customers’ email inboxes, making it a popular strategy, especially for retail businesses.
Key Elements:
- Consent and Personalization: Users must opt-in, ensuring you reach an interested audience. Offering incentives like discounts or free resources can encourage sign-ups.
- Email Service Providers: Platforms like Mailchimp, Sendinblue, ConvertKit, and GetResponse help manage and send marketing emails.
- Segmentation and Automation: Segment your email list to deliver targeted messages based on customer interests. Use automation to send emails triggered by customer behaviors, improving effectiveness.
4. Social Media Marketing
Social media marketing uses platforms like Facebook and Instagram to promote products and services. With 59% of the global population active on social media, it’s an excellent channel for broad reach and customer engagement.
Types of SMM:
- Organic Social Media: Posting content for your followers to engage with, relying on shares and hashtags for visibility. This helps build your brand’s reputation but has limited reach due to evolving algorithms.
- Paid Social Media: Paying platforms to boost content, ensuring it reaches a targeted audience likely to engage.
Best Practices:
Focus on the platforms where most of your audience is active and use a mix of organic and paid strategies for maximum impact.
5. Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing is about partnering up with famous people who have significant followers and reputations to promote your products. This strategy effectively boosts brand awareness, visibility, and trust, as 63% of consumers trust influencers’ recommendations more than those from brands. Working with reputable influencers is essential.
Types of Influencers:
Influencers operate on various platforms and can include celebrities, industry experts, or content creators. They are typically paid per post, with costs depending on the size of their audience.
Benefits:
- Builds brand awareness and trust.
- Influencers with loyal followers can drive sales through their recommendations.
- Cost-effective, with 60% of marketers finding it delivers better ROI than traditional advertising.
In the past, marketers primarily focused on commercials, but now they invest in a variety of videos designed to entertain and educate their target audience.
Marketers are turning to TikTok, YouTube, and Instagram to connect with younger audiences who favor social video over search engines.
Short-form video is delivering the best ROI and is expected to grow the most in 2025, with a quarter of marketers planning to invest heavily in it.
6. Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing allows individuals to promote your business in exchange for a commission. Promoters, such as influencers, bloggers, or everyday people, use referral codes to track conversions, like sales or sign-ups, and earn commissions for successful referrals.
Benefits:
- Payment is based on results, with no upfront cost.
- Boosts brand awareness and visibility.
Check out more digital marketing types here.
Traditional Marketing
In contrast to digital marketing, where everything is implemented online, traditional marketing is about enhancing offline connections with customers.
1. Print Marketing
As newspapers and magazines better understand their subscribers, businesses continue to sponsor content like articles and photography in publications their audience reads.
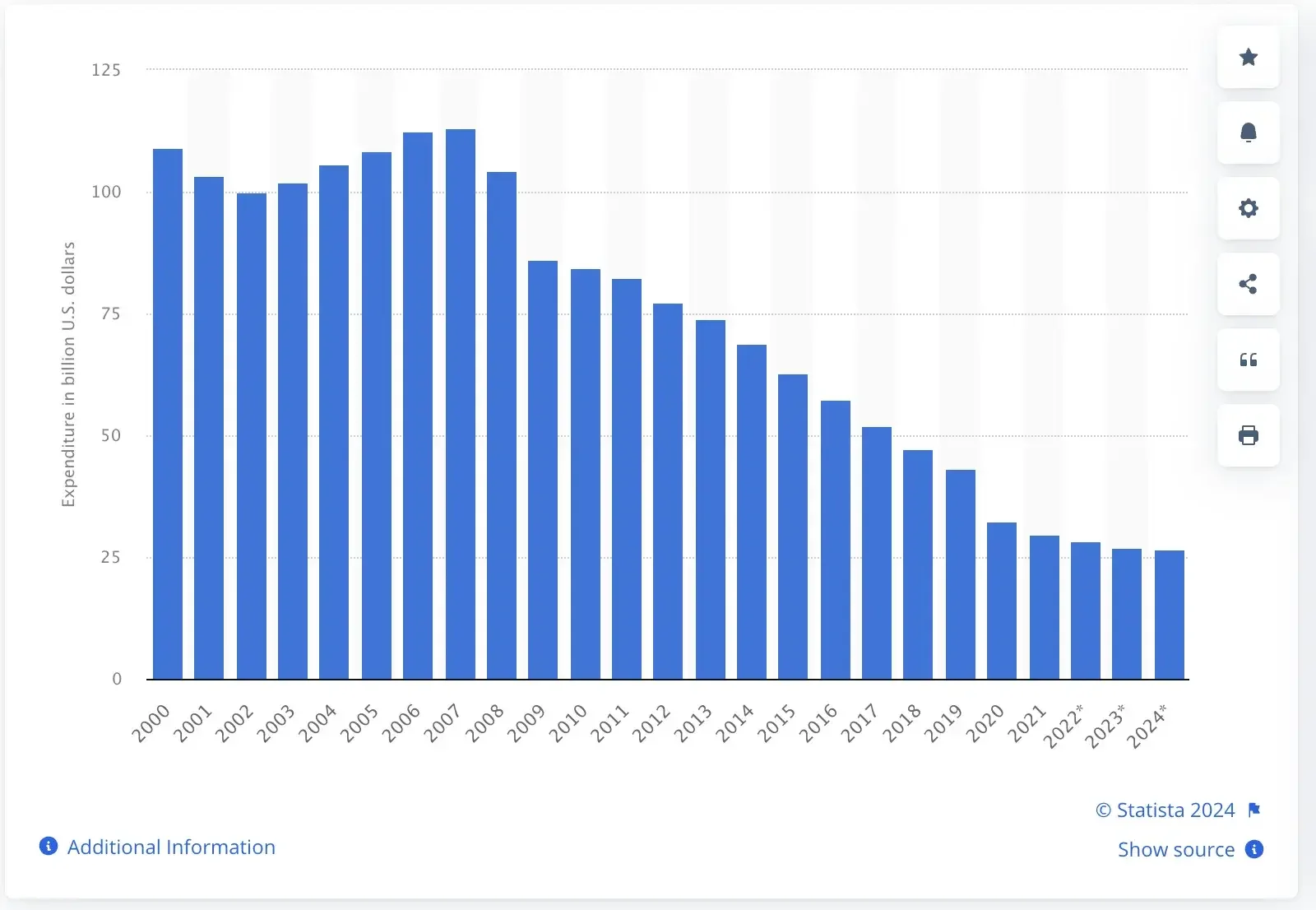
However, print marketing has declined significantly. Digital marketing has taken over, with global newspaper ad spending dropping to $28.3 billion in 2022, down from $113 billion in 2007 (Source from Statista).
2. Broadcast Marketing
With platforms like Netflix on the rise, demand for TV and radio has decreased but hasn’t disappeared. Broadcasting remains a key marketing strategy because it reaches large audiences and has a high barrier to entry, making it less accessible to small businesses.
TV ads are costly, while radio ads are more affordable but still pricier than many traditional methods. These channels are excellent for announcing offers and boosting brand awareness. Unlike posters, radio ads, for instance, are harder to ignore, as listeners often hear them while driving.
3. Event Marketing
Keep this tactic in mind for post-pandemic strategies—it’s a powerful way to connect directly with your audience. Event marketing takes face-to-face interaction to the next level, allowing marketers to meet large groups in their industry and showcase their products live. What could be more impactful?
Marketers often set up booths at industry events or even host their own to boost visibility among potential clients.
Consistently participating in events can significantly benefit your brand by increasing recognition, expanding your network, and gaining referrals as people become more familiar with your business.
4. Cold Calls Marketing
Cold calls are one of the most basic and polarizing marketing strategies. While some marketers find them intrusive and frustrating, they remain highly effective when done right.
Today, marketers have better tools to make cold calls more successful. The goal is to turn cold calls into warm ones by gathering relevant information, especially for higher-value products.
A good cold calling list should include more than just names and numbers—it should also have details like the person’s occupation, location, and competitors (for B2B). With personalization, cold calls can be much more effective, making them a valuable traditional marketing tool.
Marketing vs. Advertising
Some people misunderstand these two concepts, so we’ll summarize the main differences between them.
| Aspect | Marketing | Advertising |
|---|---|---|
| Responsibilities | - Branding - Trend analysis and competitor tracking - Customer relationship management - Cross-department alignment - Market research & strategy development - Budgeting & ROI tracking |
- Customer analysis - Pitching advertising strategies & plans - Media buying - Creative production - Campaign management - Communication between stakeholders |
| Purpose | - Lead generation - New customer acquisition - Customer retention - Consistent branding - Upsell & cross-sell management - Product development - Marketing results tracking |
- Building brand awareness - Boosting brand recognition - Attracting first-time buyers - Informing/reminding customers of your brand - Driving purchases through ads - Increasing brand loyalty - Strengthening brand image - Becoming the top-of-mind choice - Encouraging repeat purchases |
| Techniques used | - Inbound marketing: Attracting customers with organic content - Content marketing: Engaging audiences with blogs, posts, and videos - SEO: Improving rankings to drive website traffic - Email marketing: Connecting through newsletters and promotions - Affiliate marketing: Expanding reach via partner commissions |
- Traditional ads: print, TV, radio - Retail ads: shelf displays, in-store promos - Digital ads: social media, video, guest posts - Native ads: blend with webpage design, less intrusive - Billboard ads: large public displays - Mobile ads: shown in apps |
| Success measurements | - Net Promoter Score - Customer Retention - Customer Lifetime Value - Quarterly & Annual Sales Revenue - Market Share |
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) - Reach and Impressions - Click-through Rates (CTR) - Engagement - Conversion Rates |
The 4 Ps of Marketing
The 4 Ps—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—form a dynamic framework that works together to create an effective marketing strategy. Each component is equally important, and none takes precedence over the others. Instead, they collectively build a well-rounded marketing plan.
1. Product
The product is the good or service you offer to your target audience, and its success lies in either addressing an unmet need in the market or delivering a unique customer experience that creates demand. On the other hand, a strong marketing campaign must be able to show how the product appeals to their target customer.
For example, an ad for a smartphone that simply lists its technical specifications and price may not catch much attention. However, a marketer with a deep understanding of the product might create an advertisement that highlights its advanced camera features and long battery life, specifically targeting photography enthusiasts.
Some questions to ask yourself:
- What problem does your product solve? Identify the challenges your target customers face and the effects those challenges have on them.
- Who is your target customer? Define the type of individual who would benefit the most from your product.
- How does your product meet their needs? Focus on how specific features of your product directly address the demands of your audience.
- What sets your product apart from competitors? Highlight how your product solves customer problems faster, better, or more affordably than others on the market.
2. Price
The second “P” in marketing represents price, which refers to how much you should charge for your product to ensure profitability. A good starting point for your pricing strategy is to research your competitors.
Analyzing competitor pricing helps you understand what potential customers are willing to pay for your products. Pair this insight with the perceived value of your product—what your price should communicate about your brand. Does it position your product as a luxury, standard, or budget option?
Your marketing strategy can emphasize these price points accordingly. Additionally, consider incorporating popular pricing tactics like coupons, discounts, offers, or product bundles to attract more customers.
Some questions you should ask yourself when considering your product’s price are:
- What do competing products cost? Start by researching competitor prices to get an idea of your product’s price range.
- How much are customers willing to spend? Consider the maximum amount your target audience is likely to pay to establish a price cap.
- Can your product have multiple price points? Explore offering tiered pricing, such as different subscription levels or product variations, to appeal to a broader audience.
- What does your product cost to create? Calculate production or service costs to ensure your pricing allows for healthy profit margins.
3. Place
The third “P” in marketing stands for “place,” which refers to where your product or service is offered and where you should advertise to reach your target audience effectively.
For physical products or services, it’s essential to ensure they are accessible where potential customers live, shop, and work. While general marketing can work, localized strategies like investing in local SEO, advertising in community newspapers, or co-sponsoring local events may yield better results.
The same concept applies to online marketing. If your target audience includes Gen Z influencers, for instance, focusing on platforms like TikTok or Instagram will be more effective than spending your budget on platforms like Facebook or LinkedIn, which cater to older demographics.
- Where do your customers buy similar products? Consider whether your target audience prefers to shop in stores, at events, or online to identify the ideal sales channel for your product.
- Where is your customer located? Understanding where your customers live or shop is crucial for crafting an effective marketing strategy.
- Are you targeting businesses or consumers? Determine if your product is aimed at individual consumers or businesses to decide the best sales platform.
- Where do your competitors sell? Look at where successful competitors offer their products to identify the most effective places to sell your own.
4. Promotion
The fourth “P” of marketing stands for “promotion.” It’s how you communicate and advertise your product to encourage sales.
When creating your promotion strategy, consider how you want your audience to perceive your brand. For example, Disney’s marketing strategy offers valuable insights into how consistent branding, emotional storytelling, and multi-platform engagement can create an iconic global presence. Is it playful and witty, upscale and luxurious, or professional and intellectual? Establish your brand voice and maintain consistency across all marketing efforts.
Additionally, adapt your messages to fit the platform. For instance, a lengthy post might be ideal for a blog to boost SEO but won’t perform well on platforms like Facebook or Instagram. If you’re targeting users on LinkedIn and TikTok with the same message, tailor the format and tone to suit the unique audience and style of each platform.
- Who is your target audience? Identify your audience to determine the voice and tone that will resonate most effectively with them.
- How should your brand be perceived? Consider the brand personality that aligns with your product and industry.
- What channels does your audience use? Ensure your message reaches your audience by using the platforms on which they prefer to consume information.
- How are competitors promoting their products? Learn from your competitors’ successes and mistakes to refine your promotion strategy.
- Can you leverage seasonality? Adapt your marketing strategies to align with seasonal changes in your audience’s behavior.
Marketing Best Practices
Once you’ve picked your marketing strategy, you’re almost ready to launch your first campaign. But before jumping in, consider these best practices to stay on track and avoid common mistakes.
- Set clear goals: Decide what you want to achieve—more sales, website traffic, or newsletter sign-ups. Clear goals help you measure your campaign’s success and figure out what to improve.
- Know your audience: Identify who benefits most from your product. Use customer data to create profiles for each segment and tailor your content to their needs.
- Plan ahead: Create a step-by-step outline for your campaign and prepare all necessary materials in advance.
- Start soft, then follow up: Use inbound marketing by offering valuable, non-sales content to attract customers. As they move through the funnel, increase calls to action.
- Offer discounts: Coupons or discounts can encourage hesitant customers to take action and fit into your marketing budget.
- Track and analyze results: Use tools like Google Analytics or HubSpot to measure engagement and effectiveness. Use these insights to refine future campaigns.
- Shoppable posts: Can’t deny the fact that customers’ expectations are getting higher every day. People like things that are simple and quick, especially when it comes to shopping. So, make it as easy and convenient as possible for your customers to make purchases.
Wrap Up
Marketing is basically about promoting products, services, or brands to boost sales, build a strong brand image, and help businesses succeed. To achieve this, businesses need to focus on understanding their target customers.
Since customer needs and trends are always changing, sticking to the same marketing plan forever won’t work. Instead, businesses should regularly review and improve their strategies, measure campaign results, and make changes to stay competitive. This way, marketing efforts stay effective and help the business grow.





![Top 20+ Must-have Shopify Apps for 2025 [Free & Paid] - Mageplaza](https://cdn2.mageplaza.com/media/blog/must-have-shopify-apps/top-must-have-shopify-apps.png)
![[2025 Updates] Top 10+ Upsell Apps for Shopify - Mageplaza](https://cdn2.mageplaza.com/media/blog/best-upsell-shopify-app/cover.png)